Hi,
Greetings from your friend. I am going to tell you how to configure the LAN settings in various Operating Systems. First how to configure in Windows 98 and in Windows NT and then Windows XP. This will help you to configure in your Office or in your Home.
First in Windows 98.
1. Click Start the Control Panel via the Start menu.
2. Open the "Network" Control Panel.
3. This is the Network Control Panel window. You may have many more items showing. Look for this one:
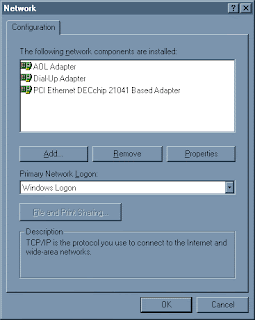

If not, look for this one:
If you don't see either of them, click the

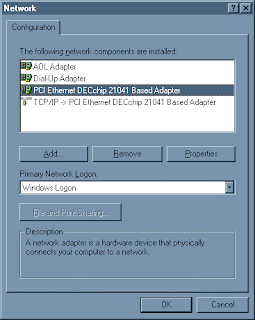
4a. If you don't have the PCI DECchip 21041 Based Adapter, select "Adapter" and click
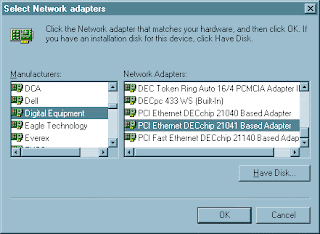
4b. Select "Digital Equipment" in the left column, then "PCI Ethernet DECchip 21041 Based Adapter" in the right hand column. Click
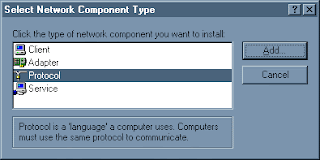
5a. You're back to this window. Now that you have the DECchip 21041 adapter installed, select "Protocol" and click
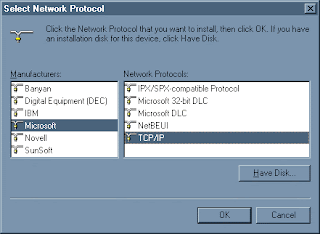
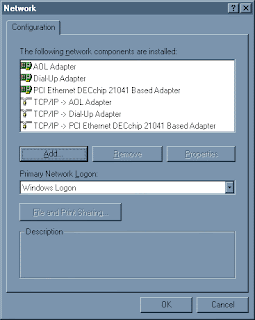
5c. You will notice that there is now a TCP/IP protocol for every adapter. You want this one
but there's one other setting to check before you work with it. Read on...
You may be able to delete the others, but you do so at your own risk.
6. Click on
then click
Be careful what you click! You must select the adapter itself, not its protocol, for this step!
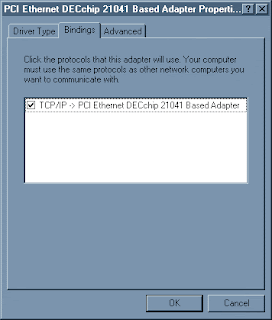
6b. Select the |Bindings| tab, make sure the box shown is checked, then click
7. Select
then click
Yeah, Windows is just like a Mac. Sure.
If you have a TCP/IP Address give it in under the option called Specify an IP address on clicking this the two text box will be enabled under this you can type the IP address and Subnet Mask.
This is the simple procedure to configure the LAN in Office or in your Home. I hope this information will help you configure the LAN.
AIX Fast Connect
Configuring Client PCs
Use the information in this chapter to connect a PC client to the AIX Fast Connect server.
TCP/IP Configuration
To access the AIX Fast Connect server, each client PC must be configured for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (RFC1001/1002), or must support direct hosting of SMB over TCP/IP (see Microsoft® Knowledge Base article 204279). Also, each client PC needs to have Client for Microsoft Networks installed. This can be accomplished for the various clients as shown in the following sections.
Windows 98 Clients
To configure Windows® 98 clients to access the AIX Fast Connect server, follow these steps:
- From the Start button, select Settings -> Control Panel -> Network.
- On the Configuration tabbed panel (initially shown), verify that the following entries exist:
- An entry for your networking-card (hardware driver)
- TCP/IP (protocol)
- Client for Microsoft Networks (client)
- Click the TCP/IP entry and select Properties.
The TCP/IP Properties dialog box has several tabbed panels. Verify the following:- IP Address panel
- Configure as needed. (For initial testing, you might want to disable DHCP and manually specify unique IP addresses for each PC.)
- Bindings panel
- Select Client for Microsoft Networks.
Additionally, you might want to enable WINS support, DNS support, or gateway support for each client. If so, configure each as needed.
- Test the client TCP/IP configuration by pinging (by IP address) from the PC client DOS prompt to the AIX Fast Connect server, and in reverse.
Windows NT Clients
To configure Windows NT® clients to access the AIX Fast Connect server, follow these steps:
- From the Start button, select Settings -> Control Panel -> Network.
- On the Adapters tabbed panel, verify that you have a correctly configured entry for your networking card (hardware driver).
- On the Services tabbed panel, verify that there are entries for the following services:
- Computer Browser
- NetBIOS Interface
- Workstation
- On the Protocols panel, add TCP/IP (if missing), then select Properties.
The TCP/IP Properties dialog box has several tabbed panels. Verify the following:- IP Address panel
- Configure as needed. (For initial testing, you might want to disable DHCP and manually specify unique IP addresses for each PC.)
You might also want to configure DNS, WINS Address, and Routing.
- Test the client TCP/IP configuration by pinging (by IP address) from the PC client DOS prompt to the AIX Fast Connect server and in reverse.
Windows XP, Windows 2003, and Windows 2000 Clients
To configure Windows 2000/XP/2003 clients to access the AIX Fast Connect server, follow these steps:
- From the Control Panel, open Network and Dialup Connections (Windows 2000) or Network Connections (Windows XP/2003).
- Right-click on the Local Area Connection icon of the network adapter to be configured. Select Properties.
- On the General tabbed panel, verify that there are checked entries for the following components:
- Your networking card entry (Windows 2000)
- Client for Microsoft Networks
- Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
- Select the TCP/IP entry, then select Properties. Configure as needed.
(For initial testing, you may want to disable DHCP and manually specify unique IP addresses for each PC.) - Test the client TCP/IP configuration by pinging (by IP address) from the PC client DOS prompt to the AIX Fast Connect server and in reverse.
NetBIOS Name Resolution
In addition to being able to ping the AIX Fast Connect server over TCP/IP, each client PC also must be able to resolve the NetBIOS name of the AIX Fast Connect server (the AIX Fast Connect servername) to an IP address. This can be done using UDP-Broadcast, LMHOSTS files, DNS, or WINS.
- UDP-Broadcast (B-node)
- The simplest NetBIOS name resolution (both in terms of setup and functionality) is UDP-Broadcast (B-node name resolution). No additional setup is required on the PC client as long as the client is on the same physical network segment (such as Ethernet or Token Ring) as the AIX Fast Connect server. The PC client broadcasts a UDP NetBIOS query to the local network, to which the AIX Fast Connect server responds. Note:This mechanism does not work across TCP/IP routers, or gateways. Larger networks typically use DNS or WINS.
- LMHOSTS files
- Windows PCs can provide local LMHOSTS files for resolving NetBIOS names. Similar to /etc/hosts on AIX, each PC can have an LMHOSTS file to statically resolve NetBIOS names to IP addresses. (This mechanism might be unsuitable for DHCP environments or networks with many client PCs, because every LMHOSTS file must change whenever the AIX Fast Connect servers' IP addresses change.)
The following is an example of editing an LMHOSTS file on Windows 98 from the DOS prompt:
C:\> cd \windows
C:\> edit lmhosts (LMHOSTS.SAM is included with Windows as an example.)On a Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows XP, or Windows 2003 machine, do the following:
C:\> cd \winnt\system32\drivers\etc
C:\> edit lmhostsAfter editing the LMHOSTS file, run the Windows PC command nbtstat -R.
- DNS
- If your network is running the domain name service (DNS) for TCP/IP and your AIX Fast Connect servername is registered in the DNS, each client PC can be configured to use DNS for NetBIOS name resolution. (This must be enabled under TCP/IP Properties for Windows NT.)
During installation, the AIX Fast Connect servername defaults to match the AIX hostname.
- WINS
- Your Windows network might use Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) for NetBIOS name resolution. Similar to DNS for TCP/IP, WINS allows NetBIOS service names to be resolved to IP addresses across multiple LAN segments. When this is the case, each Client PC is configured to use the WINS server under TCP/IP Properties.
Additionally, use the SMIT fast path smit smbcfghatt to set the WINS Address entry and Backup WINS Server for the AIX Fast Connect server. The AIX Fast Connect server uses these IP addresses to automatically register its NetBIOS server name with the WINS servers.
You can configure one or more AIX Fast Connect servers to act as NBNS/WINS servers. For more information, see NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS).
At this point, if you have LMHOSTS, DNS, or WINS correctly configured, you can ping from the client PC by using the NetBIOS server name.
Workgroups, Domains, and User Accounts
AIX Fast Connect supports several different types of user authentication/access mechanisms. (See User Administration and Basic Server Administration.) Each client PC should be configured to match the AIX Fast Connect user-access method you have chosen for your network.
For ease of use, client PCs should be in the same Windows domain as the AIX Fast Connect server (the reverse is also true). Windows NT, Windows 2000, and Windows XP all use WORKGROUP as a default workgroup name, and AIX Fast Connect server also initializes itself to use WORKGROUP. If your network uses NT domain login authentication, you can configure the AIX Fast Connect server to verify AIX Fast Connect access using the NT domain authentication servers.
Whether you use Workgroups or NT domains, access to AIX Fast Connect is managed by user security. You must set up AIX user accounts for each Windows user who is accessing AIX Fast Connect. It is easiest to use if the user accounts (and passwords) on AIX match the Windows or NT domain user accounts (and passwords).
- On the AIX Fast Connect server, use the SMIT fast path:
smit smbcfghatt
Within the SMIT panel, do the following:
- To use Workgroups, type the workgroup name in the Domain Name field.
- To use NT domain validation, type the IP addresses for the NT domain authentication server(s) in the Passthrough Authentication Server and Backup Passthrough Authentication Server fields.
- On PC clients running Windows 98, do the following:
- Select Start button -> Settings -> Control Panel -> Network.
- On the Identification panel, type the computer name for that PC.
- Configure the domain:
- To use workgroups, type the workgroup name in the Workgroup field.
- To use NT domain validation,
- On the Configuration tabbed panel, select Client for Microsoft Networks, and click Properties.
- Check the NT domain checkbox, and type the NT domain name. (To join an NT domain, you must have Domain Administrator privileges.)
- On PC clients running Windows NT, make sure you are logged in as Administrator. Then:
- Select Start button -> Settings -> Control Panel -> Network.
- On the Identification panel, select Change... .
- Type the Computer Name for that PC.
- Type the appropriate workgroup or domain name. (To join an NT domain, you must have Domain Administrator privileges.)
- On PC clients running Windows 2000, make sure you are logged in as Administrator. Then:
- Select Start button -> Settings -> Control Panel -> System.
- On the Network Identification panel, select Properties.
- Type the Computer Name for that PC.
- Type the appropriate workgroup or domain name. (To join an NT domain, you must have Domain Administrator privileges.)
- On PC clients running Windows XP or Windows 2003, make sure you are logged in as Administrator. Then follow these steps:
- From the Control Panel, choose System.
- On the Computer Name panel, select Change.
- Type the computer name for that PC.
- Type the appropriate workgroup or domain name. (To join an NT domain, you must have Domain Administrator privileges).
Enabling Windows Clients for Plain Text Passwords
For security reasons, Microsoft has disabled support for nonencrypted (plain text) network passwords in all supported versions of Windows. If you want to use plain text passwords on your network, these clients must be upgraded with the following Registry patches.
- To enable plain text passwords on Windows 98, complete the following:
- Use your favorite text editor to create the following text file, named W98plain.reg, as a local file on the Windows 98 machine:
REGEDIT4
; Registry file to allow plaintext passwords on Windows 98
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\VxD\VNETSUP]
"EnablePlainTextPassword"=dword:00000001 - Using Windows Explorer, double-click the W98plain.reg file name in the directory where you saved it. This action will update the Windows Registry for that client to allow plain text passwords.
- Shut down and restart the Windows 98 machine. (Shut down and restart is required for this patch to take effect.)
- Use your favorite text editor to create the following text file, named W98plain.reg, as a local file on the Windows 98 machine:
- To enable plain text passwords on Windows NT 4.0, log in as Administrator. Then:
- Use EDIT or the NOTEPAD accessory to create the following text file, named NT4plain.reg, as a local file on the Windows NT machine:
REGEDIT4
; Registry file to allow plaintext passwords on Windows NT 4.0
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rdr\Parameters]
EnablePlainTextPassword=dword:00000001 - Using Windows NT Explorer, double-click the NT4plain.reg file name in the directory where you saved it. This action will update the Windows Registry for that client to allow plain text passwords.
- Shut down and restart the Windows NT machine. (Shut down and restart is required for this patch to take effect.)
Note:Even with the previous patch installed, all Windows NT 4.0 clients still require users to type their password every time the user first connects to the AIX Fast Connect server (by browsing, mapping drives, and so on). After the user is successfully connected, additional browsing or drive-mapping operations proceed successfully. The initial Password Invalid message occurs because Windows NT 4.0 attempts to use encrypted passwords rather than plain text passwords, while connecting to AIX Fast Connect server. - Use EDIT or the NOTEPAD accessory to create the following text file, named NT4plain.reg, as a local file on the Windows NT machine:
- To enable plain text passwords on Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows 2003, log in as Administrator. Then:
- From the Control Panel, open Administrative Tools, then open Local Security Policy.
- On the Tree view, select Local_Policies -> Security_Options.
- On the Policy list (right-hand panel), enable the entry Send unencrypted password to connect to third-party SMB servers.
- Shut down and restart the Windows machine
Browsing the Network
AIX Fast Connect supports browser operations such as NET VIEW and Network Neighborhood (renamed My Network Places on Windows XP and Windows 2000). These operations show the user a list of file shares and printer shares exported by each server.
Network Neighborhood can also be used to map drives. To do this, right-click on a file share name, then select Map Network Drive from the menu.
- To see the AIX Fast Connect server in Network Neighborhood, a client PC needs to be able to see the Master Browser for the workgroup or domain for which that AIX Fast Connect server is configured.
Network browsing generally works best if the client PC and the AIX Fast Connect server are in the same workgroup/domain.
- The browse list database that is maintained by the Master Browser is not always up-to-date. The list can show AIX Fast Connect server names for servers that are currently down, off, physically disconnected, or otherwise unreachable. The Master Browser does not delete a server from the browse list until that server name's refresh timeout has expired, which can take several days. However, if a user tries to access that server name (by browsing share names, mapping drives, and so on), a disconnected AIX Fast Connect server is detected as unavailable.
Mapping Drives
Normally, PC clients must define drive mappings to use the AIX Fast Connect exported file shares. These drive mappings can be done from Windows or from the DOS command prompt.
You can use the following mechanisms to define or undefine mappings between PC drive letters and AIX Fast Connect file shares. For the following examples, assume that the NetBIOS server name is cifs01, and that file share apps is defined.
From DOS:
DOS> net help (help info for DOS)
DOS> net use H: \\cifs01\home (pre-defined AIX Fast Connect share)
DOS> net use F: \\cifs01\apps
DOS> copy F:\oldfile H:\newfile (uses the mapped drives)
DOS> net use F: /delete (delete the drive-mapping)
From Windows:
- In the Map Network Drive dialog box:
- Select Windows Explorer -> Tools -> Map Network Drive.
-or-
- Right-click on Network Neighborhood and select Map Network Drive.
- Select Windows Explorer -> Tools -> Map Network Drive.
- Select the drive from the Drive: drop-down list, then:
- Enter the path: (for example, \\cifs01\apps).
-or-
- Use the Shared Directories (browse tree) panel to select the network share.
- Enter the path: (for example, \\cifs01\apps).
Using AIX Fast Connect Printers
For printing, DOS and Windows mappings are somewhat different. For the following examples, assume that AIX Fast Connect server cifs01 has print shares netprint1 and pscolor defined.
For DOS applications, the following simple device-mappings can be used:
DOS> net use LPT1: \\cifs01\netprint1
DOS> net use LPT2: \\cifs01\pscolor
To test these DOS printer-mappings, use the following:
DOS> COPY text_file LPT1:
DOS> COPY Postscript_file LPT2:
For Windows applications, install a Windows printer driver and map it to the network printer, as follows:
- Select Start -> Settings -> Printers -> Add Printer.
- Select Network Printer.
- Enter the AIX Fast Connect print share name (for example, \\cifs01\netprint1) or use the browse list to select the print share.
- Select the correct Windows printer driver for that network printer (for example, IBM® 4039 Laser Printer PS), which is installed from your Windows installation disks.
Test Windows printer-driver functionality by printing a test file from any Windows application (for example, Notepad), or by using the Print Test Page feature as follows:
- Select Start -> Settings -> Printers.
- Select the printer driver (for example, pscolor).
- From the Menu Bar, select File -> Properties.
- From the tabbed panel labeled General, select Print Test Page.
Support for Windows Terminal Server
AIX Fast Connect is compatible with the Windows Terminal Server program. This program allows multiple PC clients running Windows Terminal Client software to log in to the Windows Terminal Server and establish a remote console session. Any network drive (or network printer) mapping made within that console session is forwarded by Windows Terminal Server to other NetBIOS servers, as required.
Windows Terminal Server (and other similar terminal-server programs) must accommodate multiple net mappings by multiple user names coming from multiple client PCs. Windows Terminal Server (and other terminal servers) can multiplex these requests to AIX Fast Connect using the following mechanisms:
- Multiple TCP/IP sessions (from a single Windows Terminal Server PC) to AIX Fast Connect
- Multiple SMB sessions multiplexed into a single TCP/IP session
To enable Windows Terminal Server support, set multiuserlogin=1.
If either Network Logon support or NT-passthrough authentication is enabled, Windows Terminal Server is not supported.
For specific information about setup and use of Windows Terminal Server and Windows Terminal Client, see your Windows Terminal Server documentation.
Support for Windows Active Directory Server
AIX Fast Connect can use the AIX LDAP client (ldap.client.rte) to access a Windows Active Directory Server. The cifsLdap command allows AIX Fast Connect to register and unregister its file share names and print share names into the Windows Active Directory. For more information, see the cifsLdap command.
Configuring LAN Manager authentication level
By default, AIX® Fast Connect supports the LM (LAN Manager) authentication only. AIX Fast Connect can be configured to support NTLM (NT LAN Manager) authentication instead by enabling the lm_encryption_level parameter (For details, see Appendix B. Configurable Parameters for the net Command). Most Windows clients will support either LM or NTLM authentication methods by default.
Windows 2003 clients must be specifically configured to support LM authentication.
- From the Control Panel, open Administrative Tools, then open Local Security Policy.
- On the tree view, select Local Policies -> Security Options.
- On the Policy list (right-hand panel), set the LAN Manager authentication level to Send LM & NTLM responses.
- Shut down and restart the Windows machine
No comments:
Post a Comment